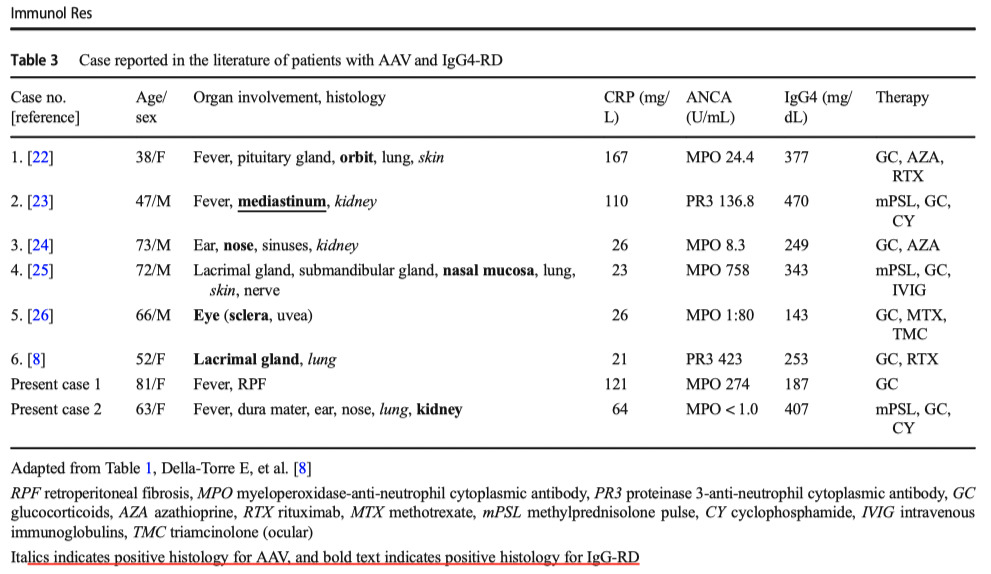
 Consideration concerning similarities and differences between ANCA-associated vasculitis and IgG-4-related diseases: case series and review of literature. Immunol Res . 2019 Feb;67(1):99-107.
Consideration concerning similarities and differences between ANCA-associated vasculitis and IgG-4-related diseases: case series and review of literature. Immunol Res . 2019 Feb;67(1):99-107.
【結論】
ANCA関連血管炎(AAV)とIgG4関連疾患(IgG4-RD)の両方の臨床的特徴を持つ2つのcaseの紹介。
AAVでは血清IgG4上昇と組織へのIgG4陽性細胞浸潤が認め、ANCA-IgG4による発症の可能性を示唆する報告もある。Nephrology. 2008;13(7):629–35.
IgG4-RDはステロイド療法が奏効するが、AAVでは免疫抑制剤の併用が必要なため、これらの疾患を区別することは重要であり診断がはっきりしない場合はオーバーラップの可能性を考慮して、追加検査も検討も必要。
【背景】
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD)IgG4関連疾患はリンパ球形質細胞の浸潤と硬化に複数の部位に起こる主ようようの腫脹が特徴的な疾患である。
IgG4-positive cellsの臓器浸潤により以下の症状が報告されている。Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(11):1982–-90.
- lacrimal gland swelling 涙腺腫脹(32.2%)
- lymphadenopathy リンパ節炎(65.3%)
- sialadenitis 唾液腺炎(64.4%)
- dacryoadenitis 涙腺炎(50.8%)
- autoimmune pancreatitis 自己免疫性膵炎 (38.1%)
- pulmonary involvement 肺病変 (27.1%)
- periaortitis/retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF) 大動脈周囲炎・後腹膜線維症 (26.3%)
- prostatitis 前立腺炎 (35.4% of male patients)
- renal involvement 腎病変 (24.6%)
- sclerosing cholangitis 硬化性胆管炎 (17.8%)
- sinusitis 副鼻腔炎 (12.7%)
抗好中球細胞質抗体(ANCA)関連血管炎(AAV)は小血管に対するpauci-immune necrotizing vasculitisを特徴とし、大きく以下の3つのタイプがある。
- microscopic polyangiitis(MPA)
- granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
- eosinophilic GPA(EGPA)
AAVによる臓器障害の多くは以下のもので、IgG4関連疾患の障害臓器とオーバーラップしているものもある。
- orbital regionl - acrimal gland swelling 涙腺腫脹(32.2%) sialadenitis 唾液腺炎(64.4%) dacryoadenitis 涙腺炎(50.8%)
- sinuses
- lungs - pulmonary involvement 肺病変 (27.1%)
- kidneys - renal involvement 腎病変 (24.6%)
- meninges
IgG4-RDとは無関係な悪性腫瘍や自己免疫疾患との関連が報告されている。Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(11):e46.
GPAの一部の患者では、IgG4-positive cellsの臓器浸潤が報告されている。Hum Pathol. 2013;44(11):2432–7.
ANCAとIgG4-RDの関係については、IgG4-RDにおけるANCA陽性の報告もある。Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(34):e4633.
【Case presentation】AAVとIgG4-RDの両方の特徴を示す2症例
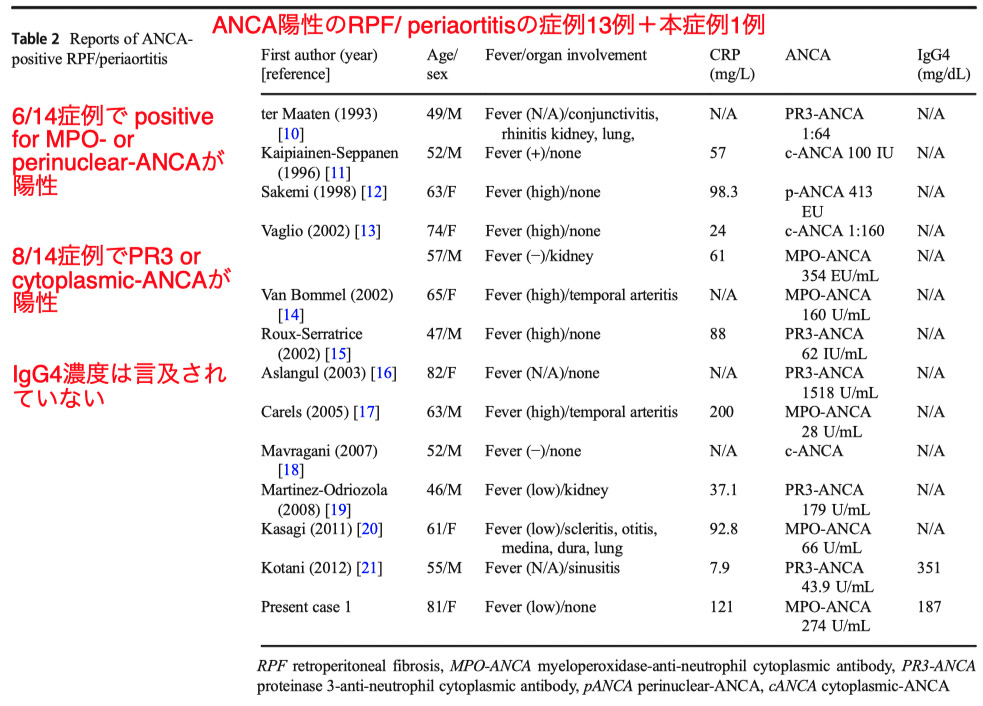
Case 1 (An 81-year-old Japanese woman)
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 108 mm/h
- C-reactive protein (CRP) level 121 mg/L
- IgG4 187.0 mg/dL
- C3 158 mg/dL
- C4 37 mg/dL
- MPO-ANCA 274 U/ mL (reference range < 3.5 U/mL)
- PR3-ANCA negative
- Urinalysis
- a microscopic hematuria of 30–49/HPF
- WBC count at 5–9/HPF
- (+/−) proteinuria
- 1 to 4 hyaline casts/LPF
- CT scan:
- bilateral hydronephrosis両側の水腎症
- soft tissue lesions surrounding the abdominal aorta腹部大動脈周囲の軟部組織病変
- findings consistent with periaortitis and RPF 大動脈周囲炎とRPFに一致する所見
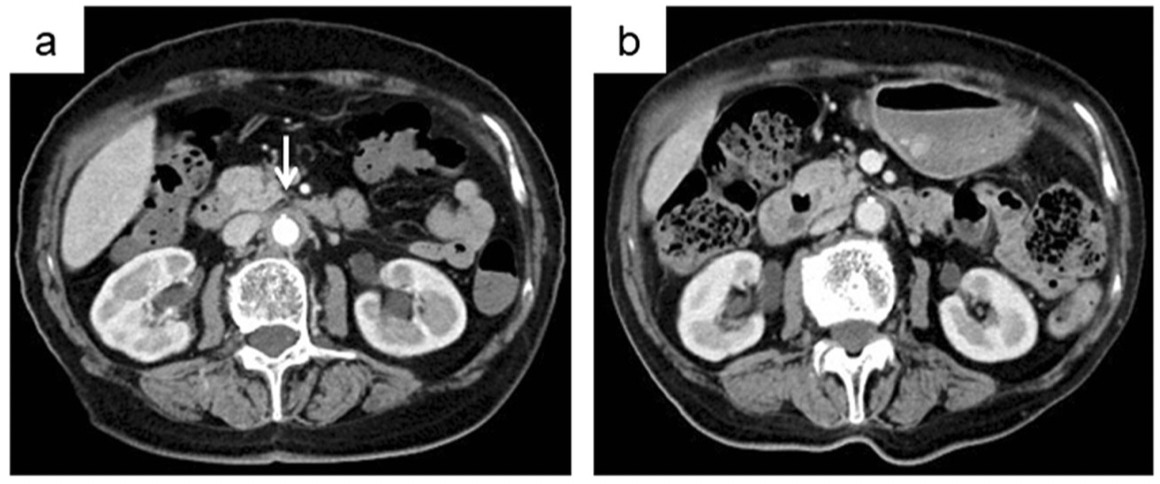
Treatment: PSL30mg開始後一ヶ月でa)→b)へ改善した。
case 2 (A 63-year-old Japanese woman)
- organizing pneumonia – PSL10mg 治療中
- loss of sensation in V2 region of trigeminal nerve
- facial weakness
- sensorineural hearing loss on the left side
- WBC count at 18200 cells/ μL
- 85% neutrophils
- 7.5% lymphocytes
- 7.5% monocytes
- ESR was 100 mm/h
- CRP level 64 mg/L
- Serum IgG4 407.0 mg/dL
- C3 134 mg/dL
- C4 48 mg/dL
- ANA, PR3-ANCA, MPOANCA all negative
- Urinalysis
- mild microscopic hematuria of 5–9/HPF
- WBC count at 5–9/HPF
- no proteinuria
- 0 to 1 hyaline casts/LPF
- β 2microglobulin 9040 μ g/L
- NAG 43.4 IU/L
- serum creatinine level 0.86→1.34 (the first 2 weeks)
- CT scan:
- right maxillary sinusitis 右上顎洞炎
- bilateral infiltration in the upper and middle lung lobes 両側の肺上葉と肺中葉に浸潤
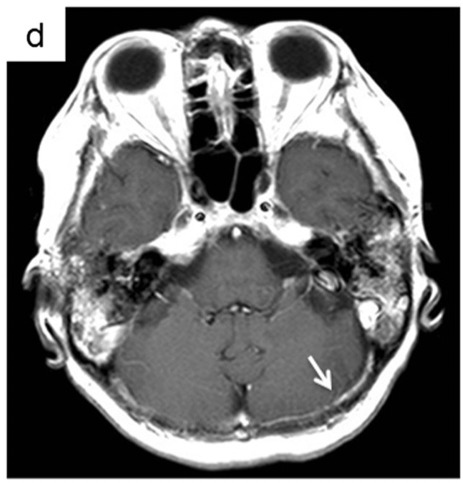
- Gadolinium-enhanced MRI : possible mild thickening of dura mater
- hypertrophic pachymeningitis 肥厚性硬膜炎
- Nasal specimens: 肉芽腫や血管炎を伴わない非特異的な慢性炎症, IgG4-positive plasma cellsの浸潤はなし
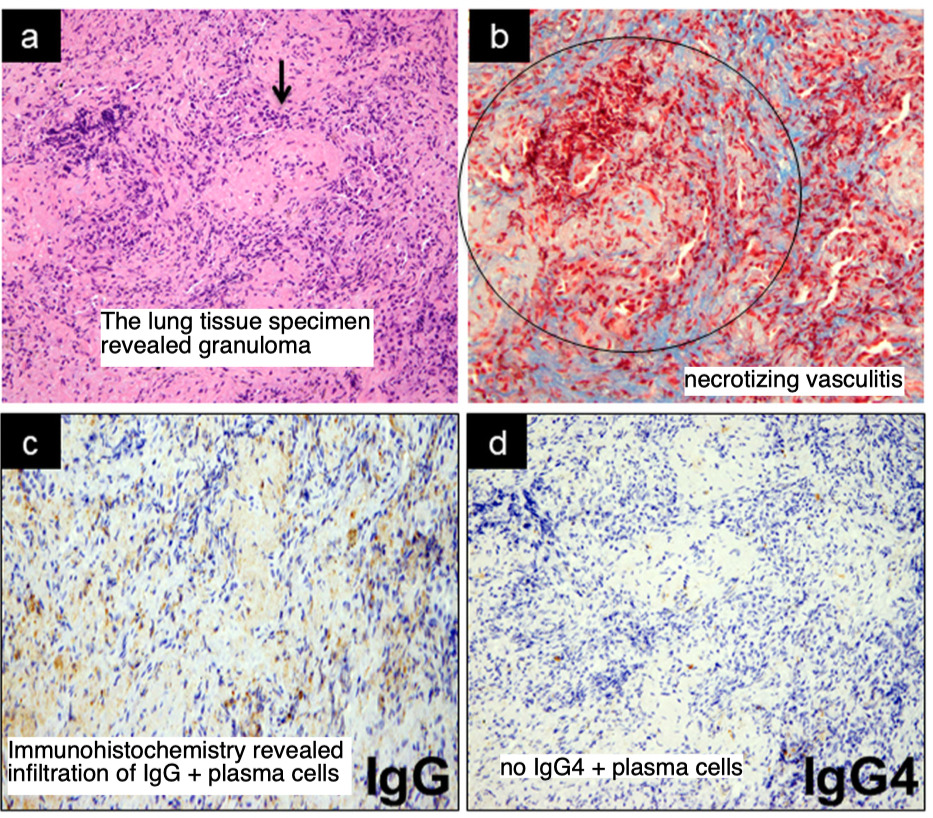
Treatment: 3日間のステロイドパルス→1mg/kg+25日目にIV-CY
【Result】
2012年3月から2017年10月までのGPA患者およびIgG4-RD患者における臨床的特徴に関する日本の単施設レトロスペクティブ分析
(診断基準)
- GPA診断:2012年改訂版Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides
Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(1):1–11 - IgG4-RD診断:2011年の包括的診断基準のover the possible Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22(1):21–30.
(Base line)
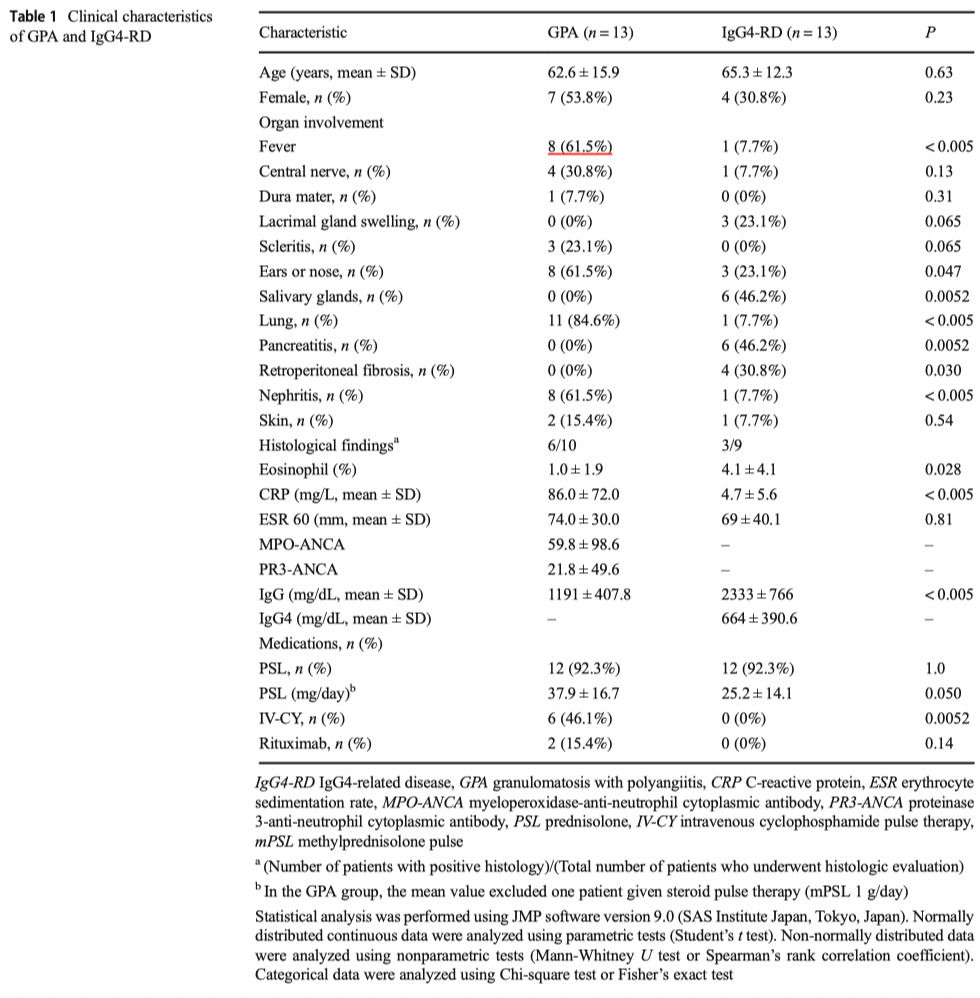
- 両群間の年齢や性別の有意差はなし
- GPA群>IgG-RD群
- Fever発熱
- ears or nose involvement耳・鼻病変
- lung involvement肺疾患
- nephritis腎炎
- CY使用
- rituximab使用
- GPA群<IgG-RD群
- salivary gland swelling唾液腺腫脹
- pancreatitis膵炎
- retroperitoneal fibrosis抗腹膜線維症
- Eosinophil count
- CRP
(病理学所見)
- GPA
- renal biopsy腎生検;necrotizing glomerulonephritis壊死性糸球体腎炎
- nasal cavity biopsy鼻腔生検:necrotizing vasculitis壊死性血管炎 or necrotizing
- granulomatous inflammation壊死性肉芽腫性炎症
- IgG-RD群
- bile duct biopsy胆管生検:lymphocytic infiltration and fibrosis(IgG4+ /IgG + cell ratio of ≥ 40%; an IgG4+ /IgG + cell ratio of ≥ 40%)
- submaxillary gland biopsy顎下腺生検:IgG4+ /IgG + cell ratio of ≥ 40%; an IgG4+ /IgG + cell ratio of ≥ 40%
- retroperitoneal biopsy後腹膜生検:lymphocytic infiltration without detectable IgG4 + cells
- renal biopsy腎生検:an IgG4+ /IgG + cell ratio of 30%
- skin biopsy皮膚生検:eukocytoclastic vasculitis白血球破砕性血管炎
【Discussion】
- ANCAとRPFの関係

- ANCA陽性RPFの特徴的な症状は、典型的なRPFと比較して、発熱や炎症マーカーの上昇であり、時に糸球体腎炎などの血管炎を併発することがある。

- RPFを伴わない場合でも、AAVとIgG4-RDの臨床的特徴がまれに共存する
- 組織学的にIgG4-RDとAAVの両方を証明したこれらの症例の特徴としては典型的なIgG4-RD症例と比較して、CRPなどの炎症マーカーがやや高い傾向にあり、免疫抑制剤をよく併用している。
- GPA症例とIgG4-RD症例のレトロスペクティブな比較分析により、両疾患の鑑別診断に有用ないくつかの相違点
- GPAでは耳鼻科領域、肺、腎臓が典型的な臓器障害であるのに対し、IgG4-RDでは涙腺・唾液腺腫脹、RPF、膵炎が典型的な臓器障害
発熱とCRPがIgG4-RDよりもGPAで有意に高い
- ANCA陽性RPFの特徴的な症状は、典型的なRPFと比較して、発熱や炎症マーカーの上昇であり、時に糸球体腎炎などの血管炎を併発することがある。
- 鑑別
- GPAでもIgG4陽性形質細胞が存在するとの報告もある。Hum Pathol. 2013;44(11):2432–7.
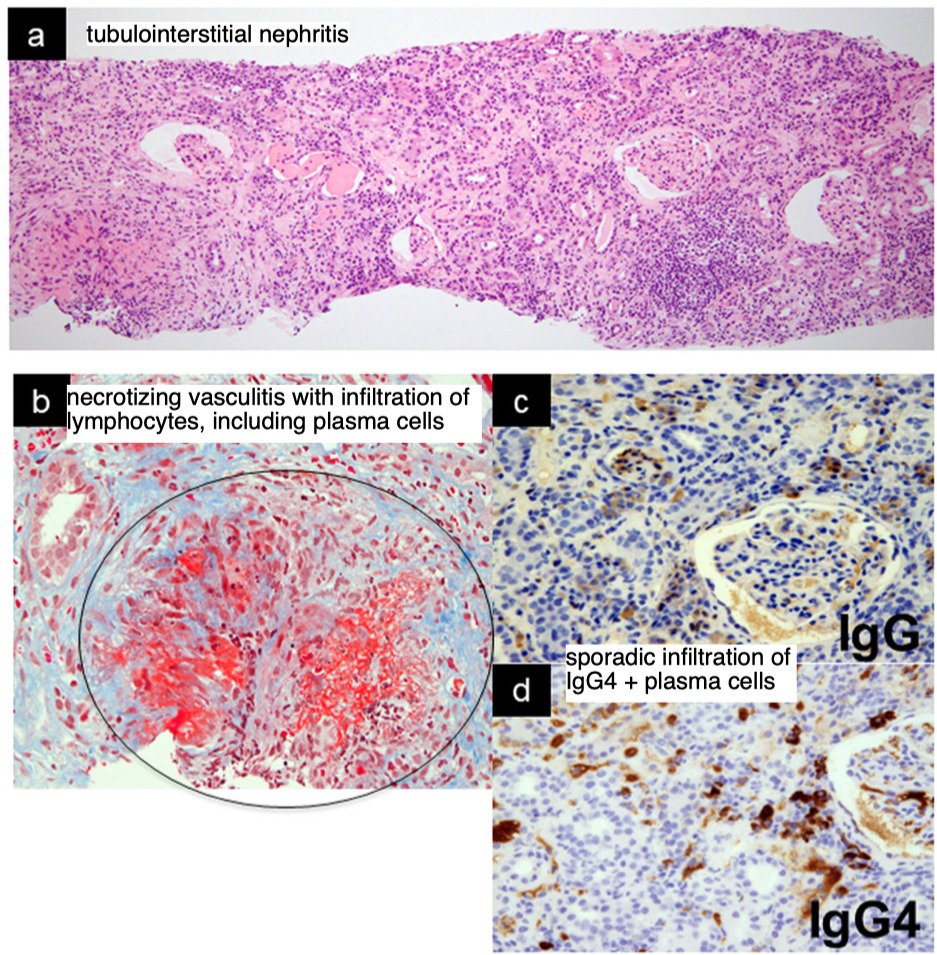
- case 2 では血液検査や臓器病変からANCA陰性GPAlikeであったが、腎病理でinterstitial nephritis primarily with IgG4-positive cells without glomerular disease糸球体疾患を伴わないIgG4陽性細胞を主体とする間質性腎炎であり、両疾患のオーバーラップの可能性は否定できない。
- 【Limitations】
Case1でetroperitoneal lesion and kidneysの病理評価ができていない。